NMT是基因功能的活体检测技术,已被103位诺贝尔奖得主所在单位,及北大、清华、中科院使用。
NMT历史上的今天
2014年01月14日,中科院水生所王强、陈辉用NMT在Plant and Cell Physiology上发表了标题为Ca2+ Signal Transduction Related to Neutral Lipid Synthesis in an Oil-Producing Green Alga Chlorella sp. C2的研究成果。'
期刊:Plant and Cell Physiology
主题:Ca2+流指示的微藻氮胁迫信号转导研究
标题:Ca2+ Signal Transduction Related to Neutral Lipid Synthesis in an Oil-Producing Green Alga Chlorella sp. C2
影响因子:4.134
检测指标:Ca2+流速
作者:中科院水生所王强、陈辉
英文摘要
Changes in the cytosolic Ca2+ levels and the role of Ca2+ signal transduction in neutral lipid synthesis in Chlorella sp. C2 under nitrogen starvation conditions were investigated. The results detected by using the scanning ion-selective electrode technique demonstrate that nitrogen starvation induced significant Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane into cells.
Ca2+ fluorescence imaging and flow cytometry were used to estimate the effect of this Ca2+ influx on the generation of the Ca2+ signal, and the results showed that the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration increased transiently and then remained at a stable, high level when the cells were exposed to nitrogen starvation. However, the increase could be inhibited by pre-treatment with the Ca2+ channel blockers ruthenium red, verapamil and GdCl3, indicating that both the influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular space via Ca2+ channels that are localized in the plasma membrane and the release of Ca2+ from intracellular calcium storage via the internal calcium store were required for the generation and transduction of the Ca2+ signal.
During nitrogen starvation, neutral lipid synthesis in Chlorella sp. C2 in response to stress conditions was also inhibited to differing degrees by pre-treatment with the three Ca2+ channel blockers, demonstrating the regulation of Ca2+ via these Ca2+ channels in neutral lipid synthesis.
The results suggested that by transduction of extracellular stress signals into the cell and the regulation of the Ca2+ signal in neutral lipid synthesis, Ca2+ signal transduction played important roles in the response mechanism of Chlorella sp. C2 to nitrogen starvation.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
小球藻中胞质Ca2+水平的变化以及Ca2+信号转导在中性脂质合成中的作用。研究了氮饥饿条件下的C2。通过使用扫描离子选择电极技术检测到的结果表明,氮饥饿导致大量Ca2+穿过质膜流入细胞。
Ca2+荧光成像和流式细胞仪用于评估这种Ca2+内流对Ca2+信号生成的影响,结果表明,当细胞暴露于细胞中时,胞浆中Ca2+的浓度会瞬时增加,然后保持稳定的高水平。氮饥饿。但是,通过用Ca2+通道阻滞剂钌红,维拉帕米和GdCl3进行预处理可以抑制这种增加,这表明Ca2+经由位于质膜上的Ca2+通道从细胞外空间大量涌入以及Ca2+的释放。Ca2+信号的产生和转导需要通过内部钙储存器进行细胞内钙储存。
在氮饥饿期间,小球藻中的中性脂质合成。通过使用三种Ca2+通道阻滞剂的预处理,C2对应激条件的响应也受到了不同程度的抑制,这表明在中性脂质合成中通过这些Ca2+通道对Ca2+的调节。
结果表明,通过将细胞外应激信号转导到细胞中以及中性脂质合成中Ca2+信号的调节,Ca2+信号转导在小球藻的反应机制中发挥了重要作用。C2导致氮饥饿。
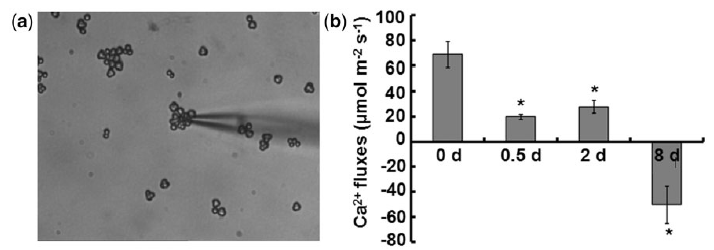
Fig. 1 The total Ca2+ flux rates over 5 min in Chlorella sp. C2 under N starvation. (a) Microphotographic examples of Ca2+ ion flux/voltage-clamp measurements. (b) Total flux rates of Ca2+ were detected at 0, 0.5, 2 and 8 d after N starvation. The columns represent the means of three replicated studies in each sample, with the SD of the means (t-test, P < 0.05). The significance of the differences between the control (0 d) and other test values was tested using a one-way analysis of variance. *P < 0.05 vs. control.
