截至目前,引用Bioss产品发表的文献共25359篇,总影响因子119363.29分,发表在Nature / Science / Cell 以及
Immunity 等顶级期刊的文献共59篇,合作单位覆盖了清华、北大、复旦、华盛顿大学、麻省理工学院、东京大学以及纽约大学等国际知名研究机构上百所。
我们每月收集引用 Bioss产品发表的文献。若您在当月已发表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,请致电Bioss,我们将赠予现金鼓励,金额标准请参考“发文章 领奖金”活动页面。
近期收录2023年6月引用Bioss产品发表的文献共305篇(图一,绿色柱),文章影响因子 (IF) 总和高达1742.4,其中,10分以上34篇(图二)。
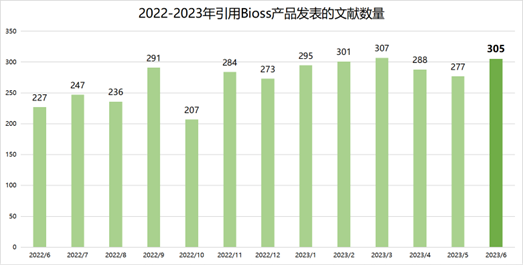
图一
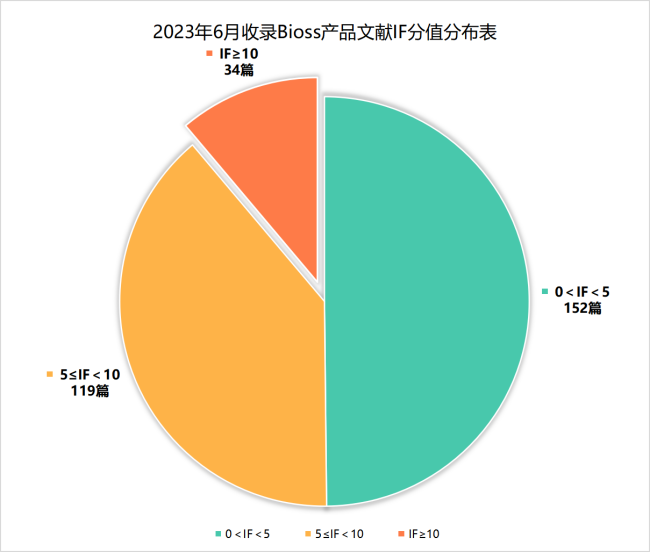
图二
本文主要分享引用Bioss产品发表文章至Nature Nanotechnology / Immunity / Cancer Cell等期刊的7篇IF>15的文献摘要,让我们一起欣赏吧
文献 1

[IF=18.2] ACS Central Science
DOI:10.1021/acscentsci.3c00377
文献引用抗体:
bs-0737R | Anti-HIF-1 Alpha pAb | WB,IHC
bs-3494R | Anti-Phospho-mTOR (Ser2448) pAb | IHC,FCM
Institution:河南大学药学院天然药物与免疫工程重点实验室
Abstract:
Changes in the cerebral microenvironment caused by
acute ischemic stroke-reperfusion are the main obstacle to the recovery of
neurological function and an important cause of stroke recurrence after
thrombolytic therapy. The intracerebral microenvironment after
ischemia-reperfusion reduces the neuroplasticity of the penumbra and ultimately
leads to permanent neurological damage. To overcome this challenge, we
developed a triple-targeted self-assembled nanodelivery system, which combines
the neuroprotective drug rutin with hyaluronic acid through esterification to
form a conjugate, and then connected SS-31, a small peptide that can penetrate
the blood brain barrier and target mitochondria. Brain targeting, CD44-mediated
endocytosis, hyaluronidase 1-mediated degradation, and the acidic environment
synergistically promoted the enrichment of nanoparticles and drug release in
the injured area. Results demonstrate that rutin has a high affinity for ACE2
receptors on the cell membrane and can directly activate ACE2/Ang1-7 signaling,
maintain neuroinflammation, and promote penumbra angiogenesis and normal
neovascularization. Importantly, this delivery system enhanced the overall
plasticity of the injured area and significantly reduced neurological damage
after stroke. The relevant mechanism was expounded from the aspects of
behavior, histology, and molecular cytology. All results suggest that our
delivery system may be an effective and safe strategy for the treatment of
acute ischemic stroke-reperfusion injury.
文献 2

[IF=16.6] Nature Communications
DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-38849-z
文献引用抗体:bs-2527R-Cy5.5 | Anti-CD163/Cy5.5 pAb | FCM
Institution:美国圣路易斯华盛顿大学医学院医学系
Abstract:
Environmental factors may alter the fetal genome to
cause metabolic diseases. It is unknown whether embryonic immune cell
programming impacts the risk of type 2 diabetes in later life. We demonstrate
that transplantation of fetal hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) made vitamin D
deficient in utero induce diabetes in vitamin D-sufficient mice. Vitamin D
deficiency epigenetically suppresses Jarid2 expression and activates the Mef2/PGC1a pathway in
HSCs, which persists in recipient bone marrow, resulting in adipose macrophage
infiltration. These macrophages secrete miR106-5p, which promotes adipose
insulin resistance by repressing PIK3 catalytic and regulatory subunits and
down-regulating AKT signaling. Vitamin D-deficient monocytes from human cord
blood have comparable Jarid2/Mef2/PGC1a
expression changes and secrete miR-106b-5p, causing adipocyte insulin
resistance. These findings suggest that vitamin D deficiency during development
has epigenetic consequences impacting the systemic metabolic milieu.
文献 3

[IF=15.1] BRAIN BEHAVIOR AND IMMUNITY
文献引用抗体:bs-0947R-FITC| Anti-ADRB2/FITC pAb | FCM
Institution:以色列特拉维夫大学萨克勒医学院临床微生物学与免疫学系
Abstract:
Stress-induced β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR)
activation in B cells increases IgG secretion; however, the impact of this
activation on antibody affinity and the underlying mechanisms remains unclear.
In the current study, we demonstrate that stress in mice following ovalbumin
(OVA) or SARS-CoV-2 RBD immunization significantly increases both serum and
surface-expressed IgG binding to the immunogen, while concurrently reducing
surface IgG expression and B cell clonal expansion. These effects were
abolished by pharmacological β2AR blocking or when the experiments were
conducted in β2AR -/- mice. In the second part of our study, we used single B
cell sorting to characterize the monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) generated
following β2AR activation in cultured RBD-stimulated B cells from convalescent
SARS-CoV-2 donors. Ex vivo β2AR activation increased the affinities of the
produced anti-RBD mAbs by 100-fold compared to mAbs produced by the same donor
control cultures. Consistent with the mouse experiments, β2AR activation
reduced both surface IgG levels and the frequency of expanded clones. mRNA
sequencing revealed a β2AR-dependent upregulation of the PI3K pathway and B
cell receptor (BCR) signaling through AKT phosphorylation, as well as an
increased B cell motility. Overall, our study demonstrates that stress-mediated
β2AR activation drives changes in B cells associated with BCR activation and
higher affinity antibodies.
文献 4

[IF=15.1] BRAIN BEHAVIOR AND IMMUNITY
文献引用抗体:
bs-20649R | Anti-PSD95 pAb | WB
bs-2723R | Anti-TREM2 pAb | FCM
Institution:国家药监局麻醉药品与精神药品研究与评价重点实验室
Abstract:
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic
condition with a high recurrence rate. To date, the clinical treatment of IBD
mainly focuses on inflammation and gastrointestinal symptoms while ignoring the
accompanying visceral pain, anxiety, depression, and other emotional symptoms.
Evidence is accumulating that bi-directional communication between the gut and
the brain is indispensable in the pathophysiology of IBD and its comorbidities.
Increasing efforts have been focused on elucidating the central immune
mechanisms in visceral hypersensitivity and depression following colitis. The
triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells-1/2 (TREM-1/2) are newly
identified receptors that can be expressed on microglia. In particular, TREM-1
acts as an immune and inflammatory response amplifier, while TREM-2 may
function as a molecule with a putative antagonist role to TREM-1. In the
present study, using the dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis model, we
found that peripheral inflammation induced microglial and glutamatergic
neuronal activation in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). Microglial ablation
mitigated visceral hypersensitivity in the inflammation phase rather than in
the remission phase, subsequently preventing the emergence of depressive-like
behaviors in the remission phase. Moreover, a further mechanistic study
revealed that overexpression of TREM-1 and TREM-2 remarkably aggravated DSS-induced
neuropathology. The improved outcome was achieved by modifying the balance of
TREM-1 and TREM-2 via genetic and pharmacological means. Specifically, a
deficiency of TREM-1 attenuated visceral hyperpathia in the inflammatory phase,
and a TREM-2 deficiency improved depression-like symptoms in the remission
phase. Taken together, our findings provide insights into mechanism-based
therapy for inflammatory disorders and establish that microglial innate immune
receptors TREM-1 and TREM-2 may represent a therapeutic target for the
treatment of pain and psychological comorbidities associated with chronic
inflammatory diseases by modulating neuroinflammatory responses.
文献 5

[IF=15.1] CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL
文献引用抗体:bs-5913R | Anti-Calreticulin pAb | IF
Institution:东南大学化学化工学院
Abstract:
Ferroptosis is an emerging antitumor treatment
modality with the superiority for evading apoptotic cell death pathway.
However, how to elevate catalytic efficacy of Fe2+-mediated Fenton reaction and
efficiently elicit ferroptosis remain enormously challenging. Herein, inspired
by hyperthermia-enhanced Fenton reaction kinetics, we firstly designed
iron-polyphenol-aspirin-coordinated nanochelates for photothermal-enhanced
ferroptosis antitumor immunotherapy. Specifically, we modulated optimal mass
feeding ratio of gallic acid (GA), aspirin (ASA), Fe (II) and
polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to construct novel nanofibrous GA-ASA-Fe (II)
metalchelates named GAFs. The variations in size and structure allowed the
nanomedicines to avoid the risk of premature renal clearance in vivo, compared
with the reported ultrasmall GA-Fe (II) nanocomplexes (GFs). Under NIR laser
irradiation, GAFs could constantly amplify toxic hydroxyl radicals (radical
dotOH) generation and deplete excessive GSH to induce more accumulation of lethal
lipid peroxidation (LPO), thereby triggering ferroptosis pathway in vitro and
in vivo. Besides, the introduction of ASA could inhibit cyclooxygenase-2
(COX-2) and prostaglandin E2
(PGE2),
in combination with photothermal-enhanced ferroptosis tumor therapy to induce
immunogenic cell death (ICD), promote maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) and
activate cytotoxic T cells for synergistic antitumor immunotherapy. GAFs with
laser irradiation exhibited the capacity of inhibition of pulmonary metastasis.
This work presented a strategy for incorporating small molecule immunomodulator
into the metal-polyphenolic coordination to ameliorate its deficiencies,
thereby inspiring a new design concept for tumor treatment.
文献 6

[IF=15.1] CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL
文献引用抗体:bs-2527R | Anti-CD163 pAb | IF,ICC
Institution:南京工业大学材料科学与工程学院
Abstract:
Smart hydrogel dressings capable of simultaneously
highly effective antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and promoting
re-epithelialization and angiogenesis are urgently needed for the management of
diabetic wounds. Herein, a H2S-releasing
multifunctional hydrogel was developed by utilizing the dynamic Schiff base
reaction between carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) and polyhexamethylene guanidine
(PHMG)-modified aldehyde F108 (PFC). Diallyl trisulfide (DATS) was encapsulated
into the PFC nanoparticles. Apart from possessing the essential properties
necessary for an idealized hydrogel dressing, such as excellent injectability,
tissue adhesion, self-healing, and stimulus–response degradation, the
DATS@PFC&CMC also utilized the synergistic effect of the PHMG and DATS to
provide an efficient antimicrobial effect; the H2S was slowly released from the DATS
under the action of GSH and exerted excellent anti-inflammatory effects, by
inhibiting the expression of p-ERK and p-STAT3 in activated macrophages, and
promoting macrophage polarization to the M2 phenotype. Strikingly, following
the completion of the efficient antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects,
the continuously generated H2S
further significantly accelerated the proliferation, migration, and
vascularization of endothelial cells by extending the activation of the p-p38
and p-ERK1/2. Owing to superior performances, DATS@PFC&CMC significantly
promoted the healing of diabetic wounds induced by streptozotocin with good
biocompatibility. This study demonstrates that DATS@PFC&CMC is a versatile
hydrogel dressing with great potential for the management of diabetic wounds.
文献 7

[IF=15.1] CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL
文献引用抗体:
bs-43042P | Recombinant SARS-Cov-2 Spike S1 protein (L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y,
R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y), His (HEK293)
bs-43049P | Recombinant SARS-Cov-2 Spike S1 protein (T19R, G142D, del157/158,
L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R), His (HEK293)
bs-43041P | Recombinant SARS-Cov-2 Spike S1 protein (D80A, D215G, del241/243,
K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G), His (HEK293)
Institution:哈尔滨医科大学生物医学学院
Abstract:
Biosensors are rapid and portable detection devices
with great potential for the instant screening of infectious diseases.
Receptors are the critical element of biosensors. They determine the
specificity, sensitivity and stability. However, current receptors are mainly
limited to antibodies and aptamers. Herein, we developed a glycosylated
extracellular vesicle-like receptor (GlycoEVLR) for the rapid detection of
virus antigens, specifically using SARS-CoV-2 as a model. The human
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)-overexpressed and heparin-functionalized
HEK-293T cell membrane-cloaked Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared as
functionalizing GlycoEVLR. They were characterized as spherical core–shell
structures with a diameter of around 100 nm, which were perfectly comparable to
natural extracellular vesicles. Binding affinities between GlycoEVLR and spike1
(S1) antigen were demonstrated using surface plasmon resonance (SPR). The
GlycoEVLR was fixed on magnetic electrodes to construct electrochemical
biosensors. Using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) as a measurement
technique, the S1 antigen was detected down to 1 pg/mL within 20 min and showed
a good linearity range from 1 pg/mL to 1 ng/mL. Also, the GlycoEVLR-based
electrochemical biosensors showed excellent antifouling performance and
stability. Overall, our work provides a useful methodology for developing
extracellular vesicle-like receptors for biosensors. Combining the inherit
natural receptor proteins and antifouling lipids from the host cells with
engineered glycan motifs to target and sense viral antigens will open a new avenue
for biosensors.
